Several web based genome annotation services have been developed in recent years which make it easy to determine gene functions based on genome sequences. However, the functional annotation results from different services are often not the same and a scheme to obtain consensus functional annotations by integrating different results is in demand. Prof Ma Hongwu at Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, collaborating with researchers from the University of Edinburgh, recently published a paper on "BMC Bioinformatics" to address this demand. They presented a semi-automated scheme to compare functional annotations from different sources and consequently obtain a consensus genome annotation. They compared the annotation results from four services(RAST, JCVI, IMG, IGS) and Multiple techniques from information retrieval were used to preprocess the raw functional annotations. A decision tree based method was used to obtain a consensus functional annotation result. This approach can greatly reduce the workload of manual comparison by automatically comparing and determining >80% of the functional annotations. It was applied to six phylogenetically different genomes and the results showed that the consensus annotation obtained by data integration was more accurate and reliable than those from individual services. 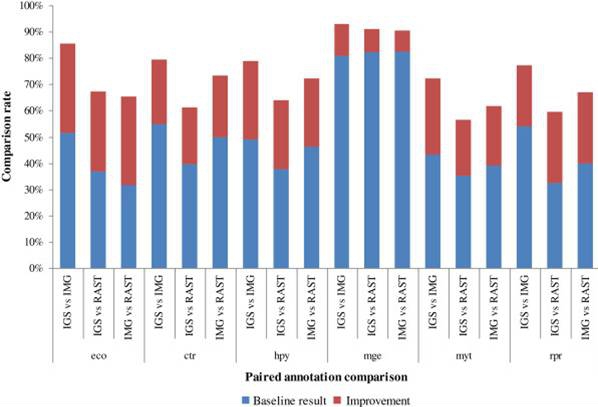
|