Dr. Huaming Wang's group identified a new low temperature lipase that can be used for detergent market
November 20, 2013 ------ the laboratory of Dr. Huaming Wang filed a patent application with the title of "a lipase and its application" in collaboration with a biotech company named “Vland Biotech Group”
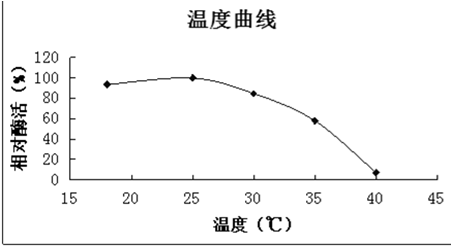
Lipase (EC 3.1.1.3), also known as glycerol hydrolase, is the enzymes that hydrolyzing carboxylic ester bonds of triglycerides to produce glycerol diesters, monoglyceride, fatty acids and glycerol. The broad spectrum of the substrate/Special specificity of the lipase make it widely used in fields of detergent, food processing, ester bond formation and chiral pharmaceuticals component synthesis. Lipase has become the third largest industrial enzymes after the proteases and amylases. Currently, the detergent lipase exhibits only the high temperature properties.
In this work, Dr. Wang’s lab first sequenced a new genome of Stachybotrys chartarum in collaboration with Dr. Zhugen Chen’s lab. Through the genome analysis, they have identified a new lipase with low homologous to other known lipases. Dr. Wang’s group then expressed this new lipase in their filamentous fungi, Aspegillus niger under the strong inducible promoter. The enzyme sample preparations were tested in a detergent condition for removal of the oil stains. The result showed a better performance than the lipase marketed by the international enzyme company.
This work was sponsored by the Vland Biotech Group, a leading enzyme fermentation company in China as part of research collaboration between “Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology” and “Vland Biotech Group” in a form of “Jointed Research Laboratory”.
