Allitol is a rare polyol found in nature that is useful not only as a sweetener, but also as the raw material for production of chemical compounds. It may be an important intermediate for the preparation of some medicines against diabetes, cancer, and viral infections, including AIDS. Moreover, allitol is located at the center of hexoses in the Izumoring strategy, a new concept for the bioproduction of all hexose sugars. Thus, allitol could be useful as a substrate for the production of L-form ketoses and aldoses.
The Lab of Functional Sugar and Natural Bioactive Products led by Professor SUN Yuanxia at Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a novel strain K. oxytoca G4A4 isolated from soil. It could facilitate the conversion of d-psicose to allitol (rate of 87%) using resting cells of G4A4. Futhermore, the gene of D-ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) from K. oxytoca and D-psicose-3-epimerase (DPE) from Ruminococcus sp. were characterised and coexpressed to form the multi-enzyme coupling pathway for allitol production in E. coli. The formate dehydrogenase (FDH) with RDH constituted the cofactor recycling system for supplying NADH, and the membrane protein GLF was introduced to increase the intracellular concentration of substrate (D-fructose). Finally, a recombinant E. coli strain was constructed for the conversion of D-fructose to allitol via intermediate of D-psicose, and the maximum yield of allitol was 48.62 g/L using the whole-cell biotransformation system. The results showed that the recombinant strain had enormous potential for application in the production of allitol.
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101303), and the study entitled ”Construction of allitol synthesis pathway by multi-enzyme coexpression in Escherichia coli and its application in allitol production” was published on Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology. ZHU Yueming, research associate, is the first author.
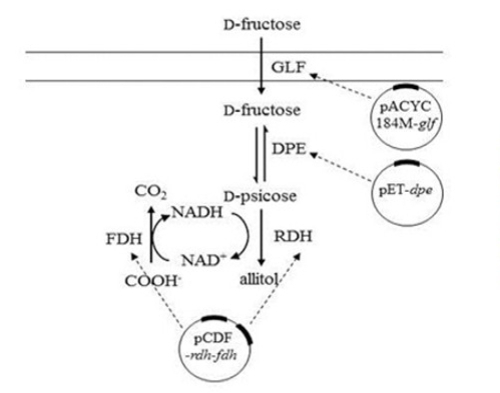
The strategy for allitol production using whole-cell biotransformation (Image by Prof. SUN Yuanxia’s group)
Contact:
SUN Yuanxia
Email: sun_yx@tib.cas.cn